Psalm 8 Verse-by-Verse
Welcome to the Verse-by-Verse Notes for Psalm 8!
The Verse-by-Verse Notes present scholarly, exegetical materials (from all layers of analysis) in a verse-by-verse format. They often present alternative interpretive options and justification for a preferred interpretation. The Verse-by-Verse Notes are aimed at consultant-level users.
The discussion of each verse of this psalm includes the following items.
- A link to the part of the overview video where the verse in question is discussed.
- The verse in Hebrew and English.[1]
- An expanded paraphrase of the verse.[2]
- A grammatical diagram of the verse, which includes glosses for each word and phrase.[3]
- A series of notes on the verse, which contain information pertaining to the interpretation of the psalm (e.g., meaning of words and phrases, poetic features, difficult grammatical constructions, etc.).
Superscription (v. 1)
v. 1
| v. | Hebrew | Close-but-clear |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | לַמְנַצֵּ֥חַ עַֽל־הַגִּתִּ֗ית מִזְמ֥וֹר לְדָוִֽד׃ | For the director. On the gittith. A psalm by David. |
Expanded Paraphrase
For the director, on the gittith, a psalm by David to whose offspring YHWH promised to give universal dominion.
Grammatical Diagram with Phrase-level Glosses
SimpleGrammar
DiscourseUnit [v.1] <showGlosses="1">
Fragment
Clause
Predicate
Adverbial
PrepositionalPhrase
Preposition
preposition: לַ for
Object
article: ה the <status="elided">
Nominal
verb-participle: מְנַצֵּחַ director
Fragment
Clause
Predicate
Adverbial
PrepositionalPhrase
Preposition
preposition: עַל on
Object
article: הַ the
noun: גִּתִּית gittith
Fragment
Nominal
noun: מִזְמוֹר psalm
Fragment
PrepositionalPhrase <gloss="by David">
Preposition
preposition: לְ of >> by
Object
noun: דָוִד David
Notes
- The word gittith (גִּתִּית) occurs in the heading of Psalms 8, 81, and 84. The meaning of this word is unknown. It might refer to the name of either a musical instrument or a tune from the Philistine city Gath.[4] This view is supported by the Targum, כינורא דאייתי מגת[5] (“the lute that he brought from Gath”)[6] as well as by Rashi, כְּלִי זֶמֶר שֶׁבָּא מִגַּת[7] (“a musical instrument that came from Gath”). Since David spent some time as a vassal of the king of Gath, he could have become familiar with the instrument or tune then.[8] Some interpreters think the term גִּתִּית could actually be derived from the word גַּת meaning “winepress,”[9] in which case the term גִּתִּית would refer to “the celebration of the grape harvest at the Feast of Tabernacles.”[10] This view is supported by the LXX, ὑπὲρ τῶν ληνῶν[11] (“over the wine vats”)[12] and Jerome Gall. and Heb., Pro torcularibus[13] (“for the winepresses”).
Introduction (vv. 2-3)
Verses 2 and 3 form the first section of the psalm. The main ideas of this section are: glory bestowed by God on the heavens; and a metaphor of strength through children.
v. 2
| v. | Hebrew | Close-but-clear |
|---|---|---|
| 2a | יְהוָ֤ה אֲדֹנֵ֗ינוּ מָֽה־אַדִּ֣יר שִׁ֭מְךָ בְּכָל־הָאָ֑רֶץ | YHWH, our lord, how majestic is your name in all the earth, |
| 2b | אֲשֶׁ֥ר תְּנָ֥ה ה֝וֹדְךָ֗ עַל־הַשָּׁמָֽיִם׃ | you whose glory is bestowed on the heavens! |
Expanded Paraphrase
YHWH, our lord, you who are the great king over all creation and over your people, Israel, how majestic is your name in all the earth, you whose royal glory is bestowed on the heavens, on the sun, moon, and stars and other heavenly beings, on whom you have conferred some of your royal authority.
Grammatical Diagram with Phrase-level Glosses
SimpleGrammar
DiscourseUnit [v.2]
Fragment
Clause
Vocative
Apposition
Nominal
noun: יְהוָה YHWH
RelativeClause
RelativeParticle
particle: אֲשֶׁר who
Clause
Subject
Clause
Predicate
verb-infinitive: תְּנָה is bestowed
Object
ConstructChain <gloss="whose glory">
noun: הוֹדְ glory
suffix-pronoun: ךָ you <located="relative clause head">
Predicate
Complement
PrepositionalPhrase
Preposition
preposition: עַל on
Object
article: הַ the
noun: שָּׁמָיִם heavens
Nominal <gloss="our lord">
ConstructChain
noun: אֲדֹנֵי lord
suffix-pronoun: נוּ us
Fragment
Clause
Subject
Nominal <gloss="your name">
ConstructChain
noun: שִׁמְ name
suffix-pronoun: ךָ you
Predicate
Complement
adjective: אַדִּיר majestic
adverb: מָה how
Adverbial
PrepositionalPhrase
Preposition
preposition: בְּ in
Object
article: הָ the
noun: אָרֶץ earth
quantifier: כָל all
Notes
- The psalm begins by addressing YHWH in the second person. In fact, the entire psalm is addressed to YHWH in the second person.[14]
- YHWH is identified as our lord. A "lord" (אָדוֹן) is someone who exercises authority over a people or place.[15] Kings could be called "lords" (e.g., Gen 40:1; 1 Kgs 22:17; 1 Chr 12:20), and here in Ps 8:2 the title assumes YHWH's kingship; the word "majestic" (אַדִּיר) in v. 2a is used to describe the majesty of kings (e.g., Ps 136:18), as is the word "glory" (הוֹד) in v. 2b (e.g., Pss 21:6; 45:4).
- Following the opening address to YHWH is an exclamation; the particle How (מָה) here "functions as an introduction to an exclamation in which a speaker usually expresses a value judgment about something."[16] The value judgment which the speaker expresses is that YHWH's name is majestic.
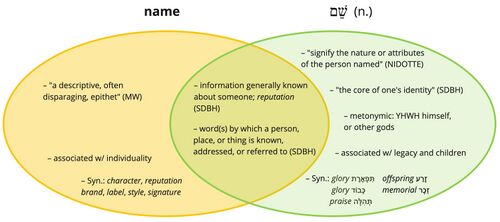
- YHWH's name (שֵׁם) is not only the word by which he is "known, addressed, or referred to," but also "the information generally known about him;"[17] "name" (שֵׁם) can signify "the nature or attributes of the person named."[18] Thus, to say that YHWH's "name" is majestic in all the earth is to say that YHWH is characterized by and known by his majesty which is on display throughout all the earth.
- The sphere of YHWH's lordship, in which his "majesty" is displayed, is all the earth.
- This is the first appearance of the word all (כֹּל), which appears four times in this psalm. It is used twice in the frame of the psalm to refer to the scope of God's dominion (vv.2b, 10b) and twice in the body of the psalm to refer to the scope of humanity's dominion (vv.7b-8a). Alter identifies כֹּל as "the chief thematic key-word of the psalm. [God's] dominion is over all, heaven and earth, angels and men and creatures of the field and air and sea, and he places 'all' at the feet of man."[19]
- The grammar and meaning of v. 2b are one of the top three exegetical issues in this psalm. See The Text, Grammar, and Meaning of Psalm8:2b and watch this part of the exegetical issues video for a detailed discussion of the issue.[20] In short, although the form תְּנָה (bestowed) looks like an imperative,[21] it is probably an infinitive construct from the root נתן (lit.: "the bestowing of your glory is on the heavens").[22] While this view is not without problems, it seems to be the least problematic of the proposed options.[23] The psalmist may have chosen the anomalous form for the sake of alliteration (compare תְּנָה and מָה) and/or to express the ongoing nature of YHWH's bestowal of glory on the heavens.[24]
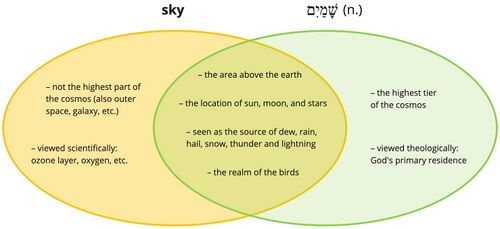
- YHWH's majesty is bestowed on the heavens. Other passages in the Bible talk about someone "bestowing" (נתן) "glory" (הוֹד) "on" (על) someone (e.g., Num 27:20 [Moses to Joshua]; Dan 11:21 [someone to new king]; 1 Chr 29:25 [YHWH to Solomon]; cf. Ps 21:6 [YHWH to king]). In each of these passages the phrase means "to confer or transmit authority," usually of a king/leader to another king/leader. Thus, it is used here to speak of "heaven as the bearer and manifestation of the divine majesty"[25] and perhaps of the dominion which YHWH has given to the heavenly bodies (cf. Gen 1:16-18) or to divine beings.[26] Some translate the phrase "above the heavens" (ESV) or "higher than the heavens" (NLT) instead of "on the heavens"[27] Yet, given the clear and consistent meaning elsewhere of נָתַן הוֹד עַל ("bestow glory on someone") as well as the fact the heavens become the object of marvel in v. 4f (which assumes that they are glorious), the interpretation "on the heavens" is to be preferred.[28] YHWH bestows "glory" (הוֹד) on the heavens (v. 2) just as he bestows "glory" (הוֹד) on humans (v. 6).
- The heavens (הַשָּׁמיִם) at the end of v. 2b is parallel with the earth (הָאָרֶץ) at the end of v. 2a. Together, the pair "heaven" and "earth" refer to the entire created world (cf. Gen 1:1) as the sphere of YHWH's lordship.
- Verse 2b is connected both to the previous line and to the following lines. As Waltke writes, "Verse 2b is a janus. It is linked to... 2a by an exceptional relative 'who,' by the Masoretic accents that retain the earliest known interpretation of the psalm, and by this parallelism: (A) I AM (B) how majestic is your name (C) in all the earth // (A') You who (B') place your splendor (C') upon the heavens."[29] There are also sound correspondences that join v. 2b and v. 2a (shamayim // shimka; tenah // mah; adir // hod). At the same time, v. 2b is connected to the body of the psalm, introducing the theme of glory on the heavens (cf. v. 4f).
v. 3
| v. | Hebrew | Close-but-clear |
|---|---|---|
| 3a | מִפִּ֤י עֽוֹלְלִ֨ים ׀ וְֽיֹנְקִים֮ יִסַּ֪דְתָּ֫ עֹ֥ז | Out of the mouths of nursing children, you have founded a fortress, |
| 3b | לְמַ֥עַן צוֹרְרֶ֑יךָ | because of your adversaries, |
| 3c | לְהַשְׁבִּ֥ית א֝וֹיֵ֗ב וּמִתְנַקֵּֽם׃ | in order to put an end to a vengeful enemy. |
Expanded Paraphrase
YHWH, you are a king, whose people are under attack by an enemy, and kings build fortresses and fortifications to repel enemy attacks. And so, you have founded a fortress to protect your people and repel the enemy. This fortress is not built on the size of your people's army or on the eloquence of their orators. Instead, it is built out of the cries that come out of the mouths of nursing children who, as the weakest and most vulnerable of the human race, represent your people as dependent on you for protection. Through their humble cries for help, you have founded a fortress because of your adversaries, in order to put an end to a vengeful enemy.
Grammatical Diagram with Phrase-level Glosses
SimpleGrammar
DiscourseUnit [v. 3]
Fragment
Clause
Predicate
verb: יִסַּדְתָּ you have founded
Object
noun: עֹז fortress
Adverbial
PrepositionalPhrase <gloss="out of the mouths of nursing children">
Preposition
preposition: מִ out of
Object
ConstructChain
noun: פִּי mouth
Nominal
verb-participle: עוֹלְלִים children
Conjunction
conjunction: וְ and
Nominal
verb-participle: יֹנְקִים nursing babies
Adverbial
PrepositionalPhrase <gloss="because of your adversaries">
Preposition
preposition: לְמַעַן on account of
Object
ConstructChain
Nominal
verb-participle: צוֹרְרֶי adversaries
suffix-pronoun: ךָ you
Adverbial
PrepositionalPhrase <gloss="in order to put an end to a vengeful enemy">
Preposition
preposition: לְ to
Object
Clause
Predicate
verb-infinitive: הַשְׁבִּית to put an end to
Object
Nominal
verb-participle: אוֹיֵב enemy
Conjunction
conjunction: וּ and
Nominal
verb-participle: מִתְנַקֵּם avenger
Notes
- The meaning of this verse is one of the top three exegetical issues. See The Meaning of Psalm8:3 and watch this part of the exegetical issues video for a detailed discussion of the issue.
- Verse 3 says that YHWH has founded a fortress (יִסַּדְתָּ עֹז).[30] The previous verse depicted YHWH as a king, and kings would build fortresses and fortifications to protect their domains from attack (cf. 1 Kgs 9:15ff; 2 Kgs 20:20; 2 Chr 17:12).
- The word translated "fortress" (עֹז) normally means "strength,"[31] but here the verb יִסַּד requires us to understand עֹז as a physical structure ("strength">"stronghold").[32]
- How has YHWH established a fortress to protect his people? The fortress comes out of the mouths of nursing children (מִפִּי עוֹלְלִים וְיֹנְקִים).[33] This prepositional phrase is fronted for marked focus.[34] In other words, YHWH has founded a fortress not by means of the powerful and eloquent, but by means of the helpless cries of the weakest and most vulnerable.
- Nursing children (עוֹלְלִים וְיֹנְקִים) represent the weakest and most vulnerable part of the human race (cf. 1 Sam 15:3; 22:29; Jer 44:7; Lam 1:16; Joel 2:16). The two nouns (lit: "children" and "nursing babies") are probably a hendiadys: "nursing children."[35] In ancient Israel, "nursing children" may have included children up to three years of age.[36]
- The parallels between vv. 2-3 and vv. 4-5 suggest that the nursing children (v. 3) stand figuratively for all of humanity (v. 5), of which they are the weakest part. Thus, "we may take 'babes and infants' as a metaphor for the weak and inherently helpless condition of human beings."[37] More specifically, the nursing children may be an image of Israel and her kings.[38]
- Mouth (פִּי) is metonymic for speech. It is through the helpless cries of children (i.e., through the desperate prayers of his people) that YHWH protects his people.
- Why has YHWH founded a fortress? According to v. 3b, YHWH has founded a fortress because of (לְמַעַן)[39] his adversaries (צוֹרְרֶיךָ). YHWH's "adversaries" may be either "historical persons and nations (Ps 2:1-3) or mythological beings and disruptive cosmic forces (Pss 74:13; 89:10; 93:3)."[40] Those who argue for the latter think that "the enemy and avenger in v. [3]c are best explained as a reference to the foes that God overcomes in the process of creation."[41] Those who argue that the adversaries are human and historical point to the use of the phrase "your adversaries" (צֹרְרֶיךָ) in Ps 74:4 and "vengeful enemy" (אויב ומתנקם) in Ps 44:17 to refer to Israel's enemies[42] along with the fact that "here, as throughout the psalms, the psalmist is fluidly able to identify personal enemies with those hostile to God" (cf. Ps 2:3).[43] This view is probably correct, and the enemies probably refer to the enemies of God's people.[44]
- The next line (v. 3c) continues to explain why YHWH has founded a fortress: in order to put an end to a vengeful enemy. Translations such as "silence" (NIV, NLT, NRSV; cf. CEV) and "still" (ESV) may be too weak. A better rendering might be "stop" (GNT), or, even better: "put an end to" (NET, JPS85; cf. LXX αναλυειν ["put down" NETS]).[45]
- The phrase vengeful enemy (אוֹיֵב וּמִתְנַקֵּם) (lit. "the enemy and the avenger" [ESV]) is probably, like "nursing children," a hendiadys ("the vindictive enemy" [NET]).[46]
- The whole verse is aptly summarised by Waltke: "The petition and praise of the meek withstand the assault of I AM's enemies against them. In sum, through the grateful praise of I AM's dependent people – not the rhetoric of eloquent orators – I AM commences his work of defending them and of slaying their attackers."[47]
Question (vv. 4-5)
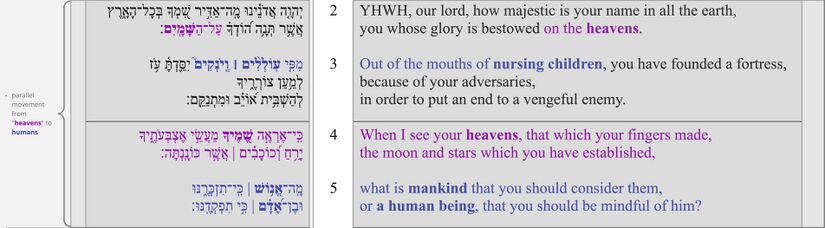
Verses 4-5 are bound together as a single syntactic unit; v. 4 is the protasis ("when..."), and v. 5 is the apodosis ("then..."). These two verses share a similar theme: the apparent insignificance of humanity (v. 5) compared with the heavens (v. 4). This section (vv. 4-5) is parallel to the previous section (vv. 2-3); both move from the heavens above (v. 2b // v. 4) to weak humans below (v. 3 // v. 5).
v. 4
| v. | Hebrew | Close-but-clear |
|---|---|---|
| 4a | כִּֽי־אֶרְאֶ֣ה שָׁ֭מֶיךָ מַעֲשֵׂ֣י אֶצְבְּעֹתֶ֑יךָ | When I see your heavens, that which your fingers made, |
| 4b | יָרֵ֥חַ וְ֝כוֹכָבִ֗ים אֲשֶׁ֣ר כּוֹנָֽנְתָּה׃ | the moon and stars which you have established, |
Expanded Paraphrase
When I look up at the night-time sky and see your heavens, that which your fingers made, the moon and stars which you have established, I am awestruck by the glory and power which you have bestowed on the heavenly realm [v. 2b] and I think.
Grammatical Diagram with Phrase-level Glosses
SimpleGrammar
DiscourseUnit [v. 4]
Fragment
Conjunction
conjunction: כִּי when
Fragment
Clause
Predicate
verb: אֶרְאֶה I see
Object
Apposition
ConstructChain <gloss="your heavens">
noun: שָׁמֶי heavens
suffix-pronoun: ךָ you
Apposition
ConstructChain <gloss="that which your fingers made">
noun: מַעֲשֵׂי works
ConstructChain
noun: אֶצְבְּעֹתֶי fingers
suffix-pronoun: ךָ you
Nominal
Nominal
noun: יָרֵחַ moon
Conjunction
conjunction: וְ and
Nominal
noun: כוֹכָבִים stars
RelativeClause
RelativeParticle
particle: אֲשֶׁר which
Clause
Predicate
verb: כּוֹנָנְתָּה you have established
Object <located="relative clause head">
Notes
- Verse 4 is a dependent temporal clause: When I see...[48] The next verse (v. 5) constitutes the "then" clause: "When I see... [then I think/exclaim] what is mankind...?[49]
- The phrase your heavens" (שָׁמֶיךָ) refers to "the heavens which you created." The pronominal suffix on שָׁמֶיךָ (your heavens) is unusual (cf. Lev 26:19; Deut 28:23; 33:28; Ps 144:5).[50] Because "your heavens" sounds unnatural in English, translations often have "the heavens."[51]
- The fact that the sun is not mentioned suggests that David is gazing at the night sky. In the ancient world, stars were associated with divine beings[52] and some people worshipped the moon and stars (cf. Deut 4:19; 17:3). Here, they are called that which your fingers made (so NET; literally "the work of your fingers" [NIV, NLT]).
v. 5
| v. | Hebrew | Close-but-clear |
|---|---|---|
| 5a | מָֽה־אֱנ֥וֹשׁ כִּֽי־תִזְכְּרֶ֑נּוּ | what is mankind that you should consider them, |
| 5b | וּבֶן־אָ֝דָ֗ם כִּ֣י תִפְקְדֶֽנּוּ׃ | or a human being, that you should be mindful of him? |
Expanded Paraphrase
"What is mankind that you should consider them, or a human being, that you should be mindful of him?" Whereas the heavens and the creatures in them are glorious and powerful, humans are weak and helpless. Why should you pay attention to us?
Grammatical Diagram with Phrase-level Glosses
SimpleGrammar
DiscourseUnit [v. 5]
Fragment
ClauseCluster
Clause
Subject
noun: אֱנוֹשׁ mankind
Predicate
Complement
noun: מָה what
SubordinateClause
Conjunction
conjunction: כִּי that
Clause
Predicate
verb: תִזְכְּרֶ you should consider
Object
suffix-pronoun: נּוּ him
Conjunction
conjunction: וּ and >> or
Clause
Subject
ConstructChain <gloss= "human being">
noun: בֶן child
noun: אָדָם human
Predicate
Complement
noun: מָה what <status="elided">
SubordinateClause
Conjunction
conjunction: כִּי that
Clause
Predicate
verb: תִפְקְדֶ you should be mindful of
Object
suffix-pronoun: נּוּ him
Notes
- The rhetorical question at the center of the psalm, what is mankind...? (מָה אֱנוֹשׁ), echoes the rhetorical question at the beginning and end of the psalm, "how majestic...!" (מָה אַדִּיר).[53] But whereas the rhetorical question in v. 2 and v. 10 conveys a positive value judgment about YHWH's majesty, the rhetorical question in v. 5 conveys a negative value judgment about humanity.[54] Compare, for example, 2 Kings 8:13, which has a similar syntactic structure and tone: "What is your servant, who is but a dog, that he should do this great thing?" (ESV).
- The כִּי clause in both v. 5a and v. 5b–that you should... (NLT, NET, NEB)– indicates result.[55]
- The two yiqtol verbs–"that you should consider... be mindful of–are habitual. "The two imperfect verbal forms in v. 4 describe God’s characteristic activity" (NET).[56]
- "With God as Agent, פקד [be mindful of] expresses an intense personal attention, including careful inspection, which triggers appropriate action, whether positive (i.e., assistance) or negative (i.e., punishment)."[57]
- The rhetorical question which concludes the first half of the psalm (vv. 2-5) is answered in the second half of the psalm (vv. 6-9).[58]
Answer (vv. 6-9)
- Verses 6 through 9 work together to form the answer or response to the question posed in the previous section. The answer comes in two parts: Mankind is crowned with honor and majesty; and God has placed everything under his feet.
- Verses 6-7 are bound together by similar syntax (the use of 2ms yiqtol verbs with he suffixes), a similar theme (the exaltation of humans), and the alternating sequence of lines that begin with tav and kaf.
- The list of animals in verses 8 and 9 ties into another of the top poetic features in this psalm, discussed in our poetic features video. Ps 8:8-9 lists three basic categories of animals: (1) land animals, domestic and wild (v. 8), (2) birds (v. 9aα), (3) fish (v. 9aβb). This taxonomy closely resembles the list of animals in Gen 1:26-28, though the two passages use slightly different terminology (עוף vs צפור for "birds" and בהמות שדי vs חיה for "wild animals"): (1) land animals, domestic and wild (2) birds, (3) fish. The parallels between Gen 1:26-28 and Ps 8 lead Waltke to conclude that "Psalm 8 is Genesis 1:26-28 set to music."[59] Similarly, Gentry says that Ps 8:6-9 is "a word-by-word commentary and meditation on Genesis 1:26-28."[60] There are some slight differences between the two lists, however. Some of the terms used for wild animals (בַּהֲמוֹת) and birds (צִפּוֹר) in Ps 8 are normally used for domestic creatures, and these words may have been chosen in order to affirm the fact that these creatures are subject to humans.[61]
- Verses 8-9 are bound together by similar syntax (appositional noun phrases), similar content (animals), and an alternating sequence of lines that begin with tsade and ayin/gimal,[62] just as the lines in vv. 6-7 begin with a patterned series of consonants.
v. 6
| v. | Hebrew | Close-but-clear |
|---|---|---|
| 6a | וַתְּחַסְּרֵ֣הוּ מְּ֭עַט מֵאֱלֹהִ֑ים | And you caused him to lack being a heavenly being by a little, |
| 6b | וְכָב֖וֹד וְהָדָ֣ר תְּעַטְּרֵֽהוּ׃ | and you crowned him with honor and majesty. |
Expanded Paraphrase
And yet you created humans as your image, and, in so doing, you caused him to lack being a heavenly being who live in the heavens at which I am gazing and on whom you have conferred glory [v. 2] by only a little, and whereas kings normally choose powerful and impressive representatives for themselves, you have chosen weak and unimpressive humanity, and you crowned him like a king with royal honor and majesty and so gave him the right to rule over your creation.
Grammatical Diagram with Phrase-level Glosses
SimpleGrammar
DiscourseUnit [v. 6]
Fragment
Conjunction
conjunction: וַ and
Fragment
ClauseCluster
Clause
Predicate
verb: תְּחַסְּרֵ you caused to lack
Object
suffix-pronoun: הוּ him
SecondObject <status="alternative">
noun: מְּעַט a little
Adverbial
noun: מְּעַט little >> by a little
Adverbial
PrepositionalPhrase <gloss="being a heavenly being">
Preposition
preposition: מֵ from
Object
noun: אֱלֹהִים being a heavenly being
Conjunction
conjunction: וְ and
Clause
Predicate
verb: תְּעַטְּרֵ you crowned
Object
suffix-pronoun: הוּ him
Adverbial <gloss="with honor and majesty">
Nominal
noun: כָבוֹד honor
Conjunction
conjunction: וְ and
noun: הָדָר majesty
Notes
- The wayyiqtol verb And you caused him to lack (וַתְּחַסְּרֵהוּ) should probably be interpreted as past tense, as most translations have done.[63]
- The evidence from Ecclesiastes 4:8 (the only other instance of the verb חסר in the piel stem) suggests that the verb וַתְּחַסְּרֵהוּ means you caused him to lack,[64] and that which is lacking is indicated by the min prepositional phrase מֵאֱלֹהִים.[65]
- If the previous point is correct, then the min prepositional phrase, from (being) a heavenly being (מֵאֱלֹהִים) "is neither comparative...[66] nor partitive... but, seeing that אלהים is never used in an abstract manner so as to be equivalent to divine essentiality, negative... so that אלהים is equivalent to מהיות אלהים, cf. 31 in 1 Sam 15:23, מעם in Isa 7:8."[67]
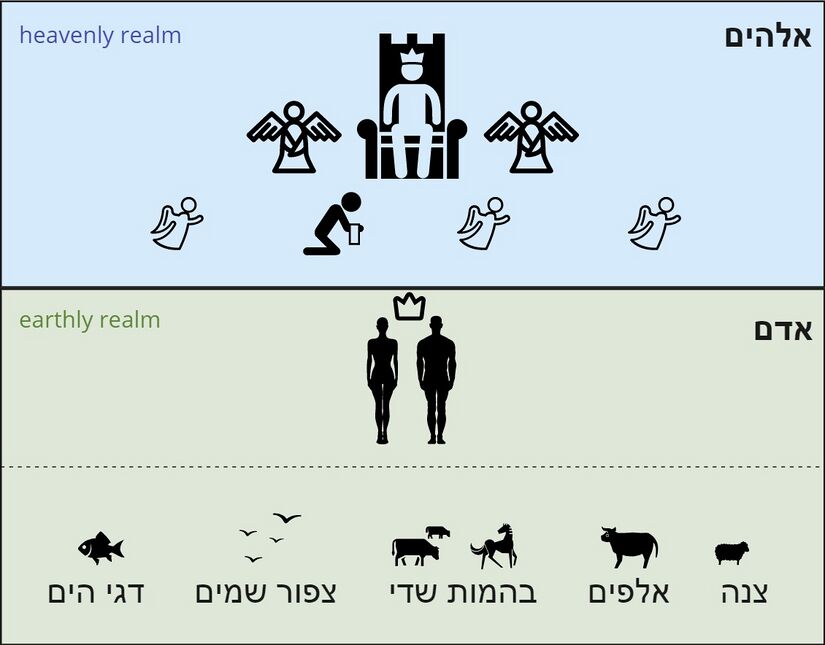
- The meaning of the word אֱלֹהִים ("God," "angels," or heavenly being?) is a top exegetical issue, discussed in detail The meaning of אלהים in Psalm 8:6 here and in our issues video exegetical issues video. In short, while many translations interpret אֱלֹהִים as a third person reference to "God"/"YHWH",[68] this interpretation is unlikely because YHWH is the second person subject of the verb. "Although Hebrew poets frequently shift their perspective from direct address to God to indirect statements about God, they do not normally alter their stance in the same clause."[69] Instead, אֱלֹהִים in Ps 8:6 is probably a "generic term for a supernatural being."[70] It refers to that class of beings which occupy the heavenly/spiritual realm (as opposed to the earthly realm), i.e. "superhuman beings including God and angels."[71]
- The meaning of Ps 8:6a is captured well by Wilson: "God has bestowed the highest possible honor on an earthly creature by creating them only a little less elevated than beings that occupy the heavenly sphere."[72] In what respect is man lower than these beings? "The writer has only this one thing in his mind, that man is inferior to God, who is רוּח, and to the angels who are רוּחות (Isaiah 31:3; Hebrews 1:14) in this respect, that he is a material being, and on this very account a finite and mortal being."[73] "In his mortality and weakness the human being stands in antithesis to God (cf. Num 23:19f.; Isa 31:3), but in his role of ruler he approximates a heavenly being."[74]
- The following yiqtol verbs–You crowned him... you caused him to rule (תְּעַטְּרֵֽהוּ / תַּ֭מְשִׁילֵהוּ) may be present/timeless,[75] future,[76] or past.[77] The h-suffix indicates that these are short yiqtols, which are (past) perfective.[78]
- The past actions recited in vv. 6-7 refer to the time when YHWH created humans as his image and gave them dominion over his creation (see Gen 1:26ff).
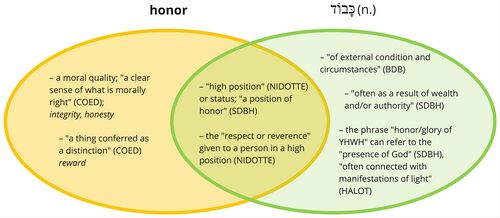
- The wearing of a crown symbolizes the right to rule (cf. 2 Kgs 11:12; cf. 2 Sam 12:26-31). "In the psalms, as in the Egyptian pictures, the king is crowned directly by God (Pss 21:3b; 132:18; cf. also 89:39). The crown signifies the manifestation and completion of the king's election (cf. Pss 5:12; 8:5; 103:4)."[79]
- Honor here refers to the "high position" which YHWH has granted humans and includes the "respect or reverence" given to those in such a position.[80]
v. 7
| v. | Hebrew | Close-but-clear |
|---|---|---|
| 7a | תַּ֭מְשִׁילֵהוּ בְּמַעֲשֵׂ֣י יָדֶ֑יךָ | You caused him to rule that which your hands made. |
| 7b | כֹּ֝ל שַׁ֣תָּה תַֽחַת־רַגְלָֽיו׃ | You placed everything under his feet. |
Expanded Paraphrase
You caused him to rule that which your hands made when you blessed him and told him to subdue the earth and rule over all of its creatures. Just as a conqueror's enemies are placed under his feet, so You placed everything under his feet.
Grammatical Diagram with Phrase-level Glosses
SimpleGrammar
DiscourseUnit [v. 7-8]
Fragment
Clause
Predicate
verb: תַּמְשִׁילֵ you caused to rule
Object
suffix-pronoun: הוּ him
Adverbial
PrepositionalPhrase <gloss="that which your hands made">
Preposition
preposition: בְּ over
Object
ConstructChain
noun: מַעֲשֵׂי works
ConstructChain
noun: יָדֶי hands
suffix-pronoun: ךָ you
Fragment
Clause
Predicate
verb: שַׁתָּה you placed
Adverbial
PrepositionalPhrase
Preposition
preposition: תַחַת under
Object
ConstructChain <gloss="his feet">
noun: רַגְלָי feet
suffix-pronoun: ו him
Object
Apposition
Nominal
quantifier: כֹּל everything
Nominal
Apposition
Nominal
noun: צֹנֶה sheep and goats
Conjunction
conjunction: וַ and
noun: אֲלָפִים cattle
Nominal
ConstructChain
Nominal <gloss="all of them">
quantifier: כֻּלָּ all
suffix-pronoun: ם them
Conjunction
conjunction: וְ and
Nominal <gloss="even wild animals">
ConstructChain
Nominal
noun: בַּהֲמוֹת land animals
Adjectival
adverb: גַם even
Nominal
noun: שָׂדָי field
Notes
- For the past tense interpretation of the verb you caused him to rule (תַּמְשִׁילֵהוּ), see the note on v. 6. The patient of the verb משל is very often indicated, as here, by a ב preposition (e.g., Gen 37:8; 45:8; Judg 9:2; Joel 2:17; etc.).
- The key word everything (כֹּל) is repeated now for the second time (see notes on v. 2). It is fronted for marked focus.[81] YHWH has subjected absolutely everything to humanity's rule; no creature has been excluded.
- To place something (or someone) under someone's feet is an expression of authority and control. When the Israelites conquered the five Amorite kings, Joshua ordered his commanders to put their feet on the necks of the conquered kings. In Psalm 110, God says to the king, “Sit at my right hand while I make your enemies your footstool.”
- The mention of feet ties in with one of this psalm's top poetic features: "Throughout the first six verses of the poem, the poet has subtly woven in a motif of vertical descent: v.2c above heavens → v.4a heavens... moon and stars → v.6a but a little lower than heavenly beings → v.6b crowned them (a reference to the head) → v.7a hands → v.7b feet..."[82] See more about this poetic feature in our From top to bottom poetic features video.
v. 8
| v. | Hebrew | Close-but-clear |
|---|---|---|
| 8a | צֹנֶ֣ה וַאֲלָפִ֣ים כֻּלָּ֑ם | Sheep and goats and cattle – all of them, |
| 8b | וְ֝גַ֗ם בַּהֲמ֥וֹת שָׂדָֽי׃ | and even wild animals, |
Expanded Paraphrase
You gave him dominion over domestic animals such as Sheep and goats and cattle – all of them, and not just domestic animals, but even wild animals,
Grammatical Diagram with Phrase-level Glosses
See previous verse for diagram.
Notes
- The phrase בַּהֲמוֹת שָׂדָי (lit.: "land animals in the field") refers here to wild animals (GNT). "Given the juxtaposition (וגם [v. 8b]) of the taxon בהמות (label 3) in Psalm 8 to two domesticated land animal subclasses, and the fact that the habitat modifier שדי is used in labels for wild land animals but not in labels for domesticated land animals, the label בהמות שדי (label 3) must refer to wild land animals."[83]
- The movement from domestic animals in the a-line to wild animals in the b-line continues the poetic feature mentioned in the previous verse. "Having descended to earth, the psalmist now changes directions and describes a horizontal vector that moves outward from human society: sheep and oxen → beasts of the field → birds → fish → whatever passes the paths of the seas."[84]
v. 9
| v. | Hebrew | Close-but-clear |
|---|---|---|
| 9a | צִפּ֣וֹר שָׁ֭מַיִם וּדְגֵ֣י הַיָּ֑ם | birds in the sky and fish in the sea, |
| 9b | עֹ֝בֵ֗ר אָרְח֥וֹת יַמִּֽים׃ | that which traverses the paths of the sea. |
Expanded Paraphrase
and not just land animals, but also birds in the sky and fish in the sea, that which traverses the paths of the sea.
As I, David, reflect on the universal dominion which you gave to humanity, I think about the universal dominion which you promised to my dynasty. You chose me, a lowly human, the least in my family, to rule over your people, Israel. My dynasty will last forever, and my descendant will reign until all his enemies are put under his feet.
Grammatical Diagram with Phrase-level Glosses
SimpleGrammar
DiscourseUnit [v. 9]
Fragment
Clause
Predicate
verb: שַׁתָּה you placed <status="elided">
Adverbial <status="elided">
PrepositionalPhrase
Preposition
preposition: תַחַת under
Object
ConstructChain <gloss="his feet">
noun: רַגְלָי feet
suffix-pronoun: ו him
Object
Apposition
noun: כֹּל everything <status="elided">
Nominal
ConstructChain <gloss="birds in the sky">
noun: צִפּוֹר small bird
noun: שָׁמַיִם sky
Conjunction
conjunction: וּ and
Apposition
Nominal
ConstructChain <gloss="fish in the sea">
noun: דְגֵי fish
Nominal
article: הַ the
noun: יָּם sea
Nominal
Clause
Predicate
verb-participle: עֹבֵר that which traverses
Object
ConstructChain <gloss="the paths of the sea">
noun: אָרְחוֹת paths
noun: יַמִּים seas
Notes
- The list of animals in this verse (birds... fish) continues the "horizontal vector that moves outward from human society: sheep and oxen → beasts of the field → birds → fish → whatever passes the paths of the seas."[85]
- "In Israelite legal, narrative, and prophetic texts, animals are often recognized as being threats to human beings (e.g., Lev 26:22; Deut 28:26; 1 Kgs 13:24; 2 Kgs 2:24; Isa 18:6; Jer 15:3)."[86] Thus, wild animals are sometimes used to depict the enemies of God's people (e.g., Pss 7:3; 10:9; 17:12; 22:13, 17, 22; 68:30; 80:14.[87] In light of v. 3 (which is about YHWH subduing Israel's enemies), the picture of YHWH placing animals under humanity's feet may be a metaphor for YHWH placing Israel's enemies under her feet (cf. Ps 144:1-3).
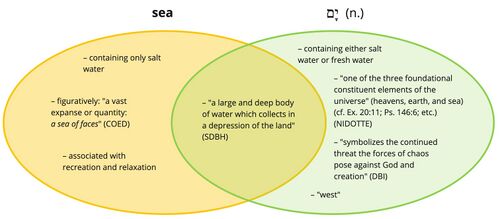
- The word sea occurs twice in this verse. About half of the repeated words refer to the spheres of divine/human dominion (land [ארץ] x2, sky [שׁמים] x3, sea [יָם] x2). As with כֹּל (see above), the emphasis is on the universality of human/divine dominion. According to Genesis 1, God created the sky (שׁמים) on Day 2, and the land (ארץ) and seas (ימים) on Day 3. These three realms together make up the cosmos. When God creates humans on Day 6, he gives them dominion over the creatures in each of these three realms (Gen 1:26 – וְיִרְדּוּ֩ בִדְגַ֙ת הַיָּ֜ם וּבְע֣וֹף הַשָּׁמַ֗יִם וּבַבְּהֵמָה֙ וּבְכָל־הָאָ֔רֶץ וּבְכָל־הָרֶ֖מֶשׂ הָֽרֹמֵ֥שׂ עַל־הָאָֽרֶץ׃).
Closing (v. 10)
Verse 10 serves as the closing to the psalm, with the repetition of, “How majestic is your name!” And so the psalm ends just as it began. And yet the same refrain which opened the psalm now takes on a new meaning. The Lord’s majesty is revealed in all the earth in a surprising way – in and through weak humans on whom he has chosen to confer glory and honor, through the likes of nursing children, whose cries to their creator and king serve to bring about an end to all chaos and disorder.
v. 10
| v. | Hebrew | Close-but-clear |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | יְהוָ֥ה אֲדֹנֵ֑ינוּ מָֽה־אַדִּ֥יר שִׁ֝מְךָ֗ בְּכָל־הָאָֽרֶץ׃ | YHWH, our lord, how majestic is your name in all the earth! |
Expanded Paraphrase
YHWH, our lord, you are not like most lords who accrue glory to themselves and abuse their subjects. Instead, you share your glory with your subjects, and you demonstrate your power in weakness. how majestic is your name in all the earth.
Grammatical Diagram with Phrase-level Glosses
SimpleGrammar
DiscourseUnit [v. 10]
Fragment
Clause
Vocative
Apposition
noun: יְהוָה YHWH
ConstructChain <gloss="our lord">
noun: אֲדֹנֵי lord
suffix-pronoun: נוּ us
Subject
ConstructChain <gloss="your name">
noun: שִׁמְ name
suffix-pronoun: ךָ you
Predicate
Adverbial
PrepositionalPhrase
Preposition
preposition: בְּ in
Object
article: הָ the
noun: אָרֶץ earth
quantifier: כָל all
Nominal
article: הָ the
noun: אָרֶץ earth
Complement
adjective: אַדִּיר majestic
adverb: מָה how
Notes
- The last line of the psalm (v. 10) repeats the first line (v. 2a) verbatim: יְהוָה אֲדֹנֵינוּ מָה־אַדִּיר שִׁמְךָ בְּכָל־הָאָרֶץ. This simple repetition is one of the psalm's top poetic features, discussed in our poetic features video. "A perfect circle is closed: the majesty of God, affirmed at the beginning, restated verbatim at the end, but with the sense accrued through the intervening eight lines of what concretely it means for His name to be majestic throughout the earth."[88] The "sense accrued" throughout the psalm is surprising. The opening declaration of Yahweh's majesty (v. 2ab) is expounded, perhaps unexpectedly, with images of helpless children (v. 3) and frail humans (v. 5). When the same words are repeated in v.10, the meaning has developed in a surprising way: Yahweh's royal majesty is manifested in weakness.
Legends
Grammatical diagram
| Visualization | Description |
|---|---|
| The clause is represented by a horizontal line with a vertical line crossing through it, separating the subject and the verb. | |
| The object is indicated by a vertical line that does not cross the horizontal line of the clause. Infinitives and participles may also have objects. If the direct object marker (d.o.m.) is present in the text, it appears in the diagram immediately before the object. If the grammar includes a secondary object, the secondary object will appear after the object, separated by another vertical line that does not cross the horizontal line of the clause. | |
| The subject complement follows the verb (often omitted in Hebrew) separated with a line leaning toward the right. It can be a noun, a whole prepositional phrase or an adjective. The later two appear modifying the complement slot. | |
| When a noun further describes or renames the object, it is an object complement. The object complement follows the object separated by a line leaning toward the right. | |
| In a construct chain, the noun in the absolute form modifies the noun in the construct form. | |
| Participles are indicated in whatever position in the clause they are in with a curved line before the participle. Participles can occur as nominal, where they take the place of a noun, predicate, where they take the place of a verb, or attributive, where they modify a noun or a verb similar to adjectives or adverbs. | |
| Infinitives are indicated by two parallel lines before the infinitive that cross the horizontal line. Infinitive constructs can appear as the verb in an embedded clause. Infinitive absolutes typically appear as an adverbial. | |
| The subject of the infinitive often appears in construct to it. In this situation, the infinitive and subject are diagrammed as a construct chain. | |
| The object of the infinitive is indicated by a vertical line that does not cross the horizontal line of the infinitival clause. | |
| Modifiers are represented by a solid diagonal line from the word they modify. They can attach to verbs, adjectives, or nouns. If modifying a verb or adjective, it is an adverb, but if modifying a noun, it is an adjective, a quantifier, or a definite article. If an adverb is modifying a modifier, it is connected to the modifier by a small dashed horizontal line. | |
| Adverbials are indicated by a dashed diagonal line extending to a horizontal line. These are nouns or infinitives that function adverbially (modifying either a verb or a participle), but are not connected by a preposition. | |
| Prepositional phrases are indicated by a solid diagonal line extending to a horizontal line. The preposition is to the left of the diagonal line and the dependent of the preposition is on the horizontal line. They can modify verbs (adverbial) or nouns (adjectival). | |
| Embedded clauses are indicated by a "stand" that looks like an upside-down Y. The stand rests in the grammatical position that the clause fulfills. Extending from the top of the stand is a horizontal line for the clause. If introduced by a complementizer, for example כִּי, the complementizer appears before the stand. Embedded clauses can stand in the place of any noun. | |
| When clauses are joined by a conjunction, they are compound clauses. These clauses are connected by a vertical dotted line. The conjunction is placed next to the dotted line. | |
| Within a clause, if two or more parts of speech are compound, these are represented by angled lines reaching to the two compound elements connected by a solid vertical line. If a conjunction is used, the conjunction appears to the left of the vertical line. Almost all parts of speech can be compound. | |
| Subordinate clauses are indicated by a dashed line coming from the line dividing the subject from the predicate in the independent clause and leading to the horizontal line of the subordinate clause. The subordinating conjunction appears next to the dashed line. | |
| Relative clauses also have a dashed line, but the line connects the antecedent to the horizontal line of the relative clause. The relative particle appears next to the dashed line. | |
| Sentence fragments are represented by a horizontal line with no vertical lines. They are most frequently used in superscriptions to psalms. They are visually similar to discourse particles and vocatives, but most often consist of a noun phrase (that does not refer to a person or people group) or a prepositional phrase. | |
| In the body of the psalm, a horizontal line by itself (with no modifiers or vertical lines) can indicate either a discourse particle or a vocative (if the word is a noun referring to a person or people group). A discourse particle is a conjunction or particle that functions at the discourse level, not at the grammatical level. Vocatives can appear either before or after the clause addressed to them, depending on the word order of the Hebrew. | |
| Apposition is indicated by an equal sign equating the two noun phrases. This can occur with a noun in any function in a sentence. |
| Hebrew text colors | |
|---|---|
| Default preferred text | The default preferred reading is represented by a black line. The text of the MT is represented in bold black text. |
| Dispreferred reading | The dispreferred reading is an alternative interpretation of the grammar, represented by a pink line. The text of the MT is represented in bold pink text, while emendations and revocalizations retain their corresponding colors (see below). |
| Emended text | Emended text, text in which the consonants differ from the consonants of the Masoretic text, is represented by bold blue text, whether that reading is preferred or dispreferred. |
| Revocalized text | Revocalized text, text in which only the vowels differ from the vowels of the Masoretic text, is represented by bold purple text, whether that reading is preferred or dispreferred. |
| (Supplied elided element) | Any element that is elided in the Hebrew text is represented by bold gray text in parentheses. |
| ( ) | The position of a non-supplied elided element is represented by empty black parentheses. For example, this would be used in the place of the noun when an adjective functions substantivally or in the place of the antecedent when a relative clause has an implied antecedent. |
| Gloss text colors | |
|---|---|
| Gloss used in the CBC | The gloss used in the Close-but-Clear translation is represented by bold blue text. |
| Literal gloss >> derived meaning | A gloss that shows the more literal meaning as well as the derived figurative meaning is represented in blue text with arrows pointing towards the more figurative meaning. The gloss used in the CBC will be bolded. |
| Supplied elided element | The gloss for a supplied elided element is represented in bold gray text. |
Shapes and colours on grammatical diagram
| Visualization | Description |
|---|---|
| The prepositional phrase is indicated by a solid green oval. | |
| The construct chain is indicated by a solid yellow oval. | |
| When the conjunction ו appears at the phrase-level (not clause-level), it is indicated by a solid light purple oval. | |
| The article is indicated by a solid blue oval. |
Expanded paraphrase
(For more information, click "Expanded Paraphrase Legend" below.)
| Expanded paraphrase legend | |
|---|---|
| Close but Clear (CBC) translation | The CBC, our close but clear translation of the Hebrew, is represented in bold text. |
| Assumptions | Assumptions which provide background information, presuppositions, entailments, and inferences are represented in italics. |
Bibliography
- Alter, Robert. 1985. The Art of Biblical Poetry. New York: Basic Books.
- Anderson, A. A. 1972. The Book of Psalms. Vol. 1. NCBC. Greenwood, SC: Attic.
- Baethgen, Friedrich. 1904. Die Psalmen. Göttingen: Vandenhoeck und Ruprecht.
- Barthélemy, Dominique. 2005. Critique Textuelle de l’Ancien Testament. Tome 4: Psaumes. Fribourg, Switzerland: Academic Press.
- Boyd, Stephen W. 2017. “The Binyanim (Verbal Stems).” In Where Shall Wisdom Be Found? A Grammatical Tribute to Professor Stephen A. Kaufman, edited by Hélène M. Dallaire, Benjamin J. Noonan, and Jennifer E. Noonan. Eisenbrauns.
- Bratcher, Robert G., and William D. Reyburn. 1991. A Translator's Handbook on the Book of Psalms. New York: UBS Handbook Series.
- Briggs, Charles and Emilie Briggs. 1906. A Critical and Exegetical Commentary on the Book of Psalms. International Critical Commentary. New York: C. Scribner’s Sons.
- Brown, William. 2002. Seeing the Psalms: A Theology of Metaphor. Louisville: Westminster John Knox Press.
- Brueggemann, Walter, and William H. Bellinger Jr. 2014. Psalms. New Cambridge Bible Commentary. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Craigie, Peter C. 2004. Word Biblical Commentary: Psalms 1–50. 2nd ed. Vol. 19. Nashville, TN: Nelson Reference & Electronic.
- Dahood, Mitchell J. 1966. The Anchor Bible: Psalms I, 1-50. Garden City, NY: Doubleday.
- Delitzsch, Franz. 1871. Biblical Commentary on the Psalms. Vol. 1. Edinburgh: T&T Clark.
- Delitzsch, Franz. 1883. A Commentary on the Psalms. New York: Funk and Wagnalls.
- Eaton, John. 2003. The Psalms: A Historical and Spiritual Commentary with an Introduction and New Translation. London; New York: T&T Clark.
- Fokkelman, J.P. 2003. Major Poems of the Hebrew Bible: At the Interface of Prosody and Structural Analysis (Vol 3: The Remaining 65 Psalms). Vol. 3. Studia Semitica Neerlandica. Van Gorcum.
- Gentry, Peter J. 1998. “The System of the Finite Verb in Classical Hebrew.” Hebrew Studies 39:7–39.
- Gentry, Peter J., and Stephen J. Wellum. 2012. Kingdom Through Covenant: A Biblical-Theological Understanding of the Covenants. Wheaton: Crossway.
- Gesenius, W. Donner, H. Rüterswörden, U. Renz, J. Meyer, R. (eds.). 2013. Hebräisches und aramäisches Handwörterbuch über das Alte Testament. Berlin: Springer.
- Hengstenberg, Ernst Wilhelm. 1863. Commentary on the Psalms. Vol. 1. Edinburgh: T. & T. Clark.
- Holmstedt, Robert D. 2016. The Relative Clause in Biblical Hebrew. Indiana: Eisenbrauns.
- Hossfeld, Frank-Lothar, and Erich Zenger. 1993. Die Psalmen I: Psalm 1–50. Neue Echter Bibel. Würzburg: Echter.
- Hupfeld, Hermann. 1855. Die Psalmen. Vol. 1. Gotha: Friedrich Andreas Perthes.
- Ibn Ezra. Ibn Ezra on Psalms.
- Jacobson, R. A. 2014. "Psalm 8," in N. DeClaissé-Walford, R. A. Jacobson & B. L. Tanner (eds.) The Book of Psalms. Grand Rapids, MI: Eerdmans.
- Jero, Christopher. 2017. “Tense, Mood, and Aspect in the Biblical Hebrew Verbal System.” In Where Shall Wisdom Be Found? A Grammatical Tribute to Professor Stephen A. Kaufman, edited by Hélène M. Dallaire, Benjamin J. Noonan, and Jennifer E. Noonan. Eisenbrauns.
- Keel, Othmar. 1997. The Symbolism of the Biblical World: Ancient Near Eastern Iconography and the Book of Psalms. Winona Lake: Eisenbrauns.
- Keener, Hubert James. 2013. A Canonical Exegesis of the Eighth Psalm: YHWH’s Maintenance of the Created Order Through Divine Reversal. Vol. 00009. Winona Lake, Indiana: Eisenbrauns.
- Kraus, Hans-Joachim. 1988. Psalms 1–59. Minneapolis: Fortress.
- Kraut, Judah. 2010. “The Birds and the Babes: The Structure and Meaning of Psalm 8.” The Jewish Quarterly Review. Vol. 100, No. 1, 10-24.
- Lunn, Nicholas P. 2006. Word-Order Variation in Biblical Hebrew Poetry: Differentiating Pragmatics and Poetics. Paternoster Biblical Monographs. Milton Keynes: Paternoster.
- Perowne, J. J. Stewart. 1870. The Book of Psalms: A New Translation with Introductions and Notes, Explanatory and Critical. Vol. I. London: Bell and Daldy.
- Robar, Elizabeth. 2013. “Wayyiqol as an Unlikely Preterite.” Journal of Semitic Studies 58 (1): 21–42.
- ________. 2015. The Verb and the Paragraph in Biblical Hebrew: A Cognitive-Linguistic Approach. Vol. 78. Studies in Semitic Languages and Linguistics. Leiden: Brill.
- Rogerson, J. W., and J. W. McKay. 1977. Psalms. Vol. 1. The Cambridge Bible Commentary on the New English Bible. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Ross, Allen P. 2011. A Commentary on the Psalms 1-41. Vol. 1. Grand Rapids, MI: Kregel.
- Sarna, Nahum M. 1993. On the Book of Psalms: Exploring the Prayers of Ancient Israel. New York: Schocken.
- Smith, Mark S. 1997. "Psalm 8:2b-3: New Proposals for Old Problems." The Catholic Biblical Quarterly. Vol. 59, No. 4, 637-641.
- Sommer, Benjamin. 2020. “Hebrew Humanism. A Commentary on Psalm 8.” 11: 7*-32*. Studies in Bible and Exegesis (עיוני מקרא ופרשנות).
- Stec, David M. 2004. The Targum of Psalms: Translated, with a Critical Introduction, Apparatus, and Notes. Collegeville, MN: Liturgical Press.
- Tate, Marvin E. 2001. "An Exposition of Psalm 8." Perspectives in Religious Studies. 28 (4), 343-359.
- Terrien, Samuel L. 2003. The Psalms: Strophic Structure and Theological Commentary. ECC. Grand Rapids: Eerdmans.
- VanGemeren, Willem. 2008. Psalms: The Expositor's Bible Commentary. Grand Rapids: Zondervan.
- Waltke, Bruce K., J. M. Houston, and Erika Moore. 2010. The Psalms as Christian Worship: A Historical Commentary. Grand Rapids, Mich: William B. Eerdmans Pub. Co.
- Whitekettle, Richard. 2006. “Taming the Shrew, Shrike, and Shrimp: The Form and Function of Zoological Classification in Psalm 8.” JBL 125: pp. 749-65.
- Wilson, Gerald H. 2002. The NIV Application Commentary: Psalms. Vol. 1. Grand Rapids: Zondervan.
- Young, Dwight W. 1960. “Notes on the Root Ntn in Biblical Hebrew.” Vetus Testamentum 10, no. 4: 457–59.
Footnotes
- ↑ The Hebrew text comes from Open Scriptures Hebrew Bible, which presents the text of the Leningrad Codex (the Masoretic text). The English text is our own "Close-but-clear" translation (CBC). The CBC is a “wooden” translation that exists to provide a window into the Hebrew text. It is essentially an interlinear that has been put into English word-order. It is also similar to a “back-translation” (of the Hebrew) often used in Bible translation checking. It is important to remember that the CBC is not intended to be a stand-alone translation, but is rather a tool for using the Layer by Layer materials. The CBC is used as the primary display text (along with the Hebrew) for most analytical visualisations. It is also used as the display text for most videos.
- ↑ A legend for the expanded paraphrase is available near the bottom of this page, in the section titled "Legends."
- ↑ Legends for both the grammatical diagram and the shapes and colours on the grammatical diagram are available near the bottom of this page, in the section titled "Legends."
- ↑ HALOT 206–207.
- ↑ CAL.
- ↑ Stec 2004, 37.
- ↑ Rashi.
- ↑ TWOT 361.
- ↑ HALOT, BDB.
- ↑ TWOT 361.
- ↑ Göttingen Hexapla Database.
- ↑ NETS.
- ↑ Weber-Gryson 1994, 776-7.
- ↑ "It is worth stressing that throughout the entire poem, the Creator is addressed directly and intimately: your name, you have established, your heavens, you remember them, and so on" (Jacobson 2014, 123).
- ↑ "אָדוֹן does not primarily denote ownership of property, but lordship over a sphere, e.g., Joseph was אָדוֹן (lord) of Pharaoh’s household and מוֹשֵׁל (ruler) of his possessions (Ps 105:21)" (NIDOTTE).
- ↑ BHRG §42.3.6, citing Ps 8:2/10 as an example.
- ↑ SDBH.
- ↑ NIDOTTE.
- ↑ Alter 1985, 119.
- ↑ See also the discussion in HALOT (1761, תנה) for a helpful overview of the interpretive options.
- ↑ In terms of morphology, the form תְּנָה looks like an imperative (cf. GKC §66h) and this view is "usually accepted" (HALOT 1761, תנה). "However, the position of this imperative after אשׁר makes it a syntactically abnormal form" (Barthélemy 2005, 22-3; cf. Baethgen 1904, 20). For this reason, some commentators (e.g., Briggs 1906, 65) consider the relative particle a secondary addition to the text. One way around this syntactic issue is to posit an elided quotative frame: "to whom (I say), 'Place your glory on the heavens!'" However, as others have noted, an imperative does not make sense in the context of the psalm, because YHWH's glory is already on the heavens (cf. v. 4) (so Hupfeld 1855, 149-153; Baethgen 1904, 20).
- ↑ So e.g., IBHS, §11.2.13b; Radak; Hengstenberg 1863, 128-9; Barthélemy 2005, 22-3 et. al.
- ↑ The infinitive construct form of נתן is usually תֵּת (cf. GKC §66h; JM §72i; BHRG §18.11.3) though the form נְתֹן occurs in Num 20:21 and Gen 38:9. The anomalous form in Ps 8 (תְּנָה) finds an analogy in the form מֵרְדָה in Gen 46:3 (רְדָה instead of רֶדֶת). According to Waltke and O'Connor, “the form תְּנָה is not an anomalous imperative of נתן but an infinitive construct, as if formed from the root יתן (the verb 'to give' has this form in Phoenician); compare ירד, infinitive construct רֵדָה” (IBHS, §11.2.13b [note 105]).
- ↑ According to this interpretation of the grammar, v.2c may be understood as a verbless clause (Subject: תנה הודך; Complement [location]: על השׁמים). “It may be interpreted: 'O Thou whose laying of Thy glory is upon the heavens...' Perhaps the author wrote תּנה הודך instead of נתתּ הודך, because he wishes to describe the setting out of the heavens with divine splendor as being constantly repeated and not as done once for all” (Delitzsch 1883, 192).
- ↑ Hupfeld 1855, 153; cf. BDB: "נָתַן הוֹד עַל put majesty upon one... so also perhaps ψ 8:2.".
- ↑ "The parallel in verse 4 suggests 'heavens' functions in this stanza as a metonymy for the heavenly host in the night sky" (Waltke 2010, 261). On the connection between "heavens" and divine beings, cf. Ps 89:6.
- ↑ Cf. GNB, DHH. Psalm 148:13 says that YHWH's majesty (הוד) is על earth and heaven, which, in light of the previous line (נשגב), it may be best to read על in the sense of "above." Cf. נתן + על in Deut 26:19; 28:1). The similarity between the two passages may support the same interpretation for Ps 8:2.
- ↑ Several translations reflect this interpretation: "you have covered the heavens with your majesty" (CSB; cf. ELB); "you reveal your majesty in the heavens above" (NET; cf. NIV, CEV; LUT; HFA, NGU).
- ↑ Waltke 2010, 258.
- ↑ Cf. NRSV, NIV, GNB, REB, CEV, NJB, RVR95, DHH, EÜ, ZÜR
- ↑ So e.g., ESV: "you have established strength."
- ↑ The prototypical meaning of יסד is "to lay the foundations" of a building or some other structure (SDBH, entry a). It may also mean, similarly, "to found -- to build; to rebuild" (SDBH, entry b). The vast majority of occurrences of the verb, in all verbal stems, may be assigned to one of these two entries. In the piel stem and pual stem, the undergoer of the action is almost always a physical structure: a house (1 Kgs 5:31; Zech 4:9; 1 Chr 6:37), a temple (Hag 2:18; Zech 8:9; Ezra 3:6, 10), a city (Josh 6:26 [Jericho]; 1 Kgs 16:34 [Jericho]; Isa 14:32 [Zion]), a stone (Isa 28:16). There is no example of an abstract noun (e.g., "strength") as the undergoer of this action. In just two instances, the verb יסד means "appoint" or "ordain" with reference to installing into office or royal decrees (Esther 1:8 [palace staff] w/על prep.; 1 Chr 9:22 [gatekeepers]). The first example has the preposition על. The second example clearly refers to the establishment of people, though it still occurs within the domain of construction. Both examples are post-exilic. Since יסד nearly always occurs in the domain of the construction of some building, and since עז can mean “a construction that is strong and able to resist attacks” (SDBH entry b; cf. BDB, HALOT, DCH), it is best to interpret the clause in Ps 8:3 to mean “you have laid the foundations for a stronghold” or “you have built a stronghold” (so e.g. BDB, NIV, RSV, CSB, GNT?). Since strongholds are designed to “resist attacks”, this interpretation works well with the following phrase: “because of your adversaries, to stop the enemy and avenger.”
- ↑ Some understand the prepositional phrase "Out of the mouths of nursing children" to modify the previous clause ("your glory is bestowed out of the mouths of nursing children") (cf. RSV, REB, GNT) rather than the following clause ("out of the mouths of nursing children you have founded a fortress"). But the oldest and best witnesses to the division of the text (Masoretic accents, LXX [cf. Matt 21:16], Syriac Peshitta, Jerome) group the phrase with the following clause.
- ↑ Lunn 2006, 296 – "MKD".
- ↑ So Zenger 1993, 79 and Brown 2002, 155. Alternatively, עוֹלְלִים וְיֹנְקִים may be a merism for children young and old (cf. 1 Sam 15:3; 22:19; Jer 44:7).
- ↑ Cf. 2 Macc 7:27: ἐλέησόν με τὴν ἐν γαστρὶ περιενέγκασάν σε μῆνας ἐννέα καὶ θηλάσασάν σε ἔτη τρία. "Have mercy on me, who carried you nine months in the womb and nursed you for three years."
- ↑ Tate 2001, 351. Cf. Benjamin Sommer: "The words 'babes and infants' are not to be taken literally but are a metaphor for the people who recite this psalm or for all humans who worship God" (Sommer 2020, 14*); cf. Zenger: "der schwächsten und wehrlosesten Gruppe im Volk JHWHs, die inmitten ihrer feindlichen Umgebung am Lobpreis JHWHs festhält" (1993, 79). Görg argues that the image in v. 3 is of humanity as "a royal child," citing Egyptian texts and statues that celebrate the rule of kings even in their infancy ("Der Mensch als königliches Kind nach Psalm 8,3" BLÄTTER ABRAHAMS 17, 2017).
- ↑ "It is an apt metaphor for ancient Israel who, trapped as a small and insignificant state between the giant superpowers of Egypt and Mesopotamia, found strength in their dependence upon their God" (Waltke 2010, 262).
- ↑ "לְמַעַן is a subordinating conjunction that is also used secondarily as a preposition" (BHRG 40.36). In this clause, where is governs only a NP, it functions as a preposition (see grammatical diagram). "The clause or noun phrase with לְמַעַן typically follows the matrix clause" (BHRG 40.36).
- ↑ Rogerson and McKay 1977, 42.
- ↑ Jacobson 2014, 123. Jacobson continues, "As is well known, the mythic concept of creation as a conflict was commonly held among Israel’s neighbors. Within the Old Testament, vestiges of this mythic idea are found... It is particularly enlightening that both Psalms 8 and 74 refer to God’s might (ʿōz; cf. Isa 51:9; Ps 89:11). The term is part of the vocabulary of the creation conflict myth, lending support to the view that the phrase you have established might because of your foes, to put an end to enemy and avenger is another reference to the act of creation" (Jacobson 2014, 123-4; cf. Anderson 1972, 102; Terrien 2003, 129).
- ↑ E.g., Baethgen 1904, 21.
- ↑ Wilson 2002, 203. Cf. 1 Sam 30:26, where Israel's enemies are called "YHWH's enemies."
- ↑ Others have argued that "no attempt should be made to sort out one type of enemy or another" and that "the enemies in this context embody whatever or whoever threatens the divine purpose of the Creator" (Tate 2001, 353). Cf. Zenger: "die pleonastische Zusammenstellung der Feindbegriffe meint alle JHWH-widrigen Mächte und Individuen" (Zenger 1993, 79).
- ↑ This verb (the hiphil of שבת) is used some 40 times. When the patient is an inanimate object or an abstract noun, it usually means "cause to cease" (e.g. Ps 46:10, Hos 2:13; see DCH שבת hiphil 1a for more examples). The verb can also mean to "destroy" or "exterminate" (BDB, DCH 1e), especially when the patient is animate (e.g., 2 Kgs 23:5, 11; Jer 36:29; Amos 8:4; Ps 119:119). This latter meaning of the verb fits the usage in Ps 8:3, where the patient is animate ("vengeful enemy") (so BDB, DCH).
- ↑ Cf. Baethgen 1904, 21; Brown 2002, 155.
- ↑ Waltke 2010, 262.
- ↑ Despite the agreement among the ancient translators that the כִּי in v. 4 is causal (LXX [οτι], Symmachus [γαρ], Peshitta [ܡܛܠ], Targum [מטול], Jerome [enim]), there is virtual unanimity among modern translations and commentators that כי here introduces a temporal clause.
- ↑ "In Ps 8:4, instead of the apodosis I exclaim which we should expect, the exclamation itself follows" (GKC 159dd; cf. IBHS 38.7a).
- ↑ There are other striking similarities between Ps 8 and Ps 144. (e.g. compare 144:3 to 8:6).
- ↑ CEV, GNT, NET, NLT.
- ↑ Cf. Job 38:7; Rev 1:20; cf. COS I:181, line 54 of the Ugaritic text "Dawn and Dusk:" "prepare (a gift) for great Shapsu and for the immutable stars."
- ↑ Note also the similarity in sound between אַדִּיר and אָדָם.
- ↑ Interrogative מה "functions as an introduction to a rhetorical question in which a speaker usually expresses a value judgment about something or someone. This value judgment is usually negative" (BHRG §42.3.6).
- ↑ "A result clause can be introduced by כי, notably after a question" (IBHS 38.3b). On מה followed by כי followed by yiqtol, cf. 1 Sam 18:18; 2 Kgs 8:13.
- ↑ This is confirmed by the n-suffixes (energic nun), which implies that the form is long yiqtol and thus imperfective aspect (Gentry 1998, 11-12; Rainey 2008, 81).
- ↑ Boyd 2017, 120-5. Cf. HALOT: "1. to make a careful inspection... e. to be troubled about, be concerned for (Isa 23:17; Jer 23:2; Zech 11:16; Ps 8:5)."
- ↑ The same structural device is used in Ps 11. The first half of the psalm (vv. 1-3) concludes with a rhetorical question which is responded to in the second half of the psalm (vv. 4-7).
- ↑ Waltke 2010, 272
- ↑ Gentry 2012, 196.
- ↑ Cf. Whitekettle 2006, 763-4.
- ↑ 'ayin was sometimes pronounced as a g sound (JM §5l; GKC §6e).
- ↑ So LXX, Tg, Syr; "you have made..." (NIV, NLT, ESV, NEB, NJB, LUT, HFA, NGÜ, EÜ, GNB, ZÜR, RVR-95); "you made..." (NET, GNT, CEV, NVI, DHH). Wayyiqtol is a sequential form that continues the semantics of the previous unit at the same level of discourse (Robar 2013, 2015). The question here is whether wayyiqtol continues (a) the semantics of the subordinate subjunctive clauses in v. 5 (>> "that you should cause him to lack") or (b) the past tense semantics of v. 3 (>> "you caused him to lack"). If the h-suffix marks perfective aspect and the n-suffix marks imperfective aspect (see Gentry 1998; Rainey 2008), then the first option is unlikely, because וַתְּחַסְּרֵהוּ has an h-suffix whereas the imperfective verbs of v. 5 have n-suffixes.
- ↑ The morphologically stative verb חסר in the qal stem can be transitive ("to lack something") or intransitive (a: "to be lacking" or b: to diminish [only in Gen 8:3, 5 according to BDB and DCH]). When the subject is a person or persons, the verb is always transitive (Gen 18:28; Deut 2:7; 8:9; 1 Kgs 11:22; Jer 44:18; Ezek 4:17; Ps 32:11; Prov 31:11), though a direct object is not grammatically required in every instance (e.g., Ps 23:1). When the subject is a thing (usually a material good), the verb is usually intransitive (1 Kgs 17:14, 16 [jar of oil]; Isa 51:14 [bread]; Eccl 9:8 [oil]; 10:3 [sense]; Song 7:3 [wine]; cf. Gen 8:3, 5 [water]). In Ps 8:6, the experiencer of the state חסר is a person (humanity). Therefore, the verb (in the piel stem) means "to cause to lack," not "to cause to be lacking" or "to cause to be less." The piel stem of verbs that are morphologically stative (like חסר) are usually factitive (i.e., the object of the verb is placed into the state indicated by the verb in the qal). "For such verbs, the Piel is an accreting stem or transitivizer, adding a core argument..." (Boyd 2017, 101).
- ↑ That which is lacked is either indicated by the noun מעט, so that the verb is ditransitive: "cause him to lack a little bit" (so GKC 117cc; Hupfeld 1853, 160f) or by the min prepositional phrase (מֵאֱלֹהִים.), as in Eccl 4:8. In the first case, מעט would be a second object on the mainline of the grammatical diagram ("you caused him to lack a little"). However, מעט can also function adverbially (see DCH מעט, sections 1bc. DCH lists Ps 8:6 as an adverbial use of מעט). This seems more likely in light of Eccl 4:8 (the only other instance of חסר in the piel stem), where חסר ("cause to be lacking") takes only one object (my soul) and the thing which is lacked is syntactically encoded not as a second object but as a min prepositional phrase (מטובה).
- ↑ Most lexicons (SDBH, DCH, HALOT) and translations, ancient (LXX, the Three) and modern (NIV, ESV, NET, CEV, GNT, NEB; LUT, HFA, NGU, ELB, EU, GNB, ZUR) seem to treat the min as comparative. This may be supported by the fact that comparative min is used with morphologically stative verbs like חסר (cf. JM §141h).
- ↑ Delitzsch 1883, 196f; cf. BDB 583.7b(b).
- ↑ E.g., Aquila, Symmachus, Theodotion, Jerome; RSV, ASV, CSB, NASB, NLT, NVI, DELUT, SCH51, EÜ, LS1910, HΡΠ.
- ↑ Waltke 2010; cf. Kraus 1988, 183; Eaton 2003, 81; Gentry Kingdom Through Covenant, 2012, 196.
- ↑ SDBH. Cf. LXX, Peshitta, Jerome, Targum, along with a number of modern translations. The LXX translation "angels" "is probably best construed as a dynamic equivalent. B. Childs says, 'The Greek translation has offered an interpretation, but one which does not in itself do an injustice to the Hebrew'" (Waltke 2010, 268).
- ↑ BDB.
- ↑ Wilson 2002, 207.
- ↑ Delitzsch 1871, 153-4.
- ↑ Waltke 2010, 268.
- ↑ ELB, cf. Goldingay 2006, 159
- ↑ Aquila, Jerome, cf. Nicacci 2006, 254; Craigie 2004, 105-6.
- ↑ LXX, Theodotion, NIV, NLT, ESV, GNT, NET, NJB, LUT, HFA, NGÜ, EÜ, ZÜR.
- ↑ Rainey 2008, 80-81. A past tense interpretation of the yiqtols is supported by the following considerations: (1) In Deut 32:10f, yiqtols with h-suffixes appear to be past perfective (cf. Jero 2017, 74). (2) The oldest extant interpretation of these verbs (LXX) understood them to be past perfective (aorist). (3) The yiqtol verbs are sandwiched between verbs that are more clearly past perfective (wayyiqtol in v. 6a and qatal in v. 7b). (4) The whole passage (vv. 6ff) is a reflection on the past act of creation.
- ↑ Keel 1997, 259.
- ↑ Cf. NIDOTTE.
- ↑ So Lunn 2006, 296 – "MKD".
- ↑ Jacobson 2014, 125.
- ↑ Whitekettle 2006, 751. The same phrase occurs in Joel 2:22.
- ↑ Jacobson 2014, 124-5; cf. Whitekettle 2006, 757-761.
- ↑ Jacobson 2014, 124-5; cf. Whitekettle 2006, 757-761.
- ↑ Whitekettle 2006, 749.
- ↑ Cf. Brown 2002, 137-144. Another clear example is Daniel's visions, wherein "one like a son of man" rules over the wild animal-like creatures that emerge from the sea and represent enemy nations.
- ↑ Alter 2011, 148.